Reflections
Reflections can be divided into two types: specular reflection and diffuse reflection. Specular reflection describes the gloss of surfaces such as mirrors, which reflect light in a simple, predictable way. This allows for the production of reflected images that can be associated with an actual (real) or extrapolated (virtual) location in space. Diffuse reflection describes non-glossy materials, such as paper or rock. The reflections from these surfaces can only be described statistically, with the exact distribution of the reflected light depending on the microscopic structure of the material. Many diffuse reflectors are described or can be approximated by Lambert’s cosine law, which describes surfaces that have equal luminance when viewed from any angle. Glossy surfaces can give both specular and diffuse reflection.
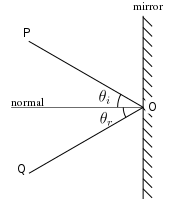
In specular reflection, the direction of the reflected ray is determined by the angle the incident ray makes with the surface normal, a line perpendicular to the surface at the point where the ray hits. The incident and reflected rays and the normal lie in a single plane, and the angle between the reflected ray and the surface normal is the same as that between the incident ray and the normal. This is known as the Law of Reflection.
For flat mirrors, the law of reflection implies that images of objects are upright and the same distance behind the mirror as the objects are in front of the mirror. The image size is the same as the object size. The law also implies that mirror images are parity inverted, which we perceive as a left-right inversion. Images formed from reflection in two (or any even number of) mirrors are not parity inverted. Corner reflectors produce reflected rays that travel back in the direction from which the incident rays came.This is called retroreflection.
Mirrors with curved surfaces can be modelled by ray tracing and using the law of reflection at each point on the surface. For mirrors with parabolic surfaces, parallel rays incident on the mirror produce reflected rays that converge at a common focus. Other curved surfaces may also focus light, but with aberrations due to the diverging shape causing the focus to be smeared out in space. In particular, spherical mirrors exhibit spherical aberration. Curved mirrors can form images with a magnification greater than or less than one, and the magnification can be negative, indicating that the image is inverted. An upright image formed by reflection in a mirror is always virtual, while an inverted image is real and can be projected onto a screen.

Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!